Fluxgate Magnetometer
A fluxgate magnetometer is a device used to measure an external magnetic field
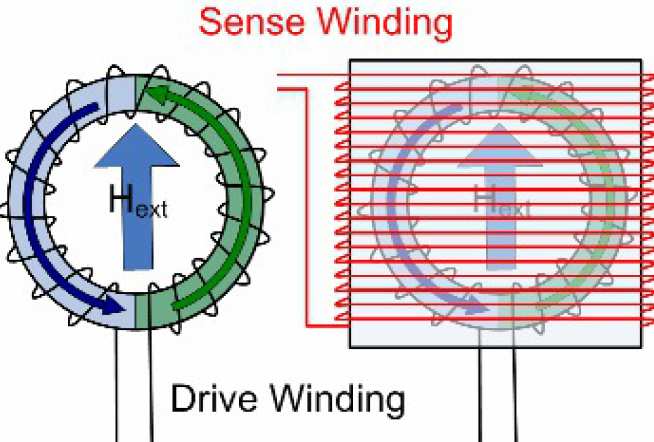
In a typical fluxgate, a drive winding coils around a magnetically permeable core that is typically toroidal. This winding delivers AC current that induces an oscillating magnetic field. With no external field, there’s no change in net flux. However, the introduction of an external field will throw off the strength of the directions of magnetic fields induced by the AC current. This creates a net flux
A sense winding is wound over the drive winding and core to pick up the induced current caused by the net flux. The induced voltage that shows up is a signal with twice the drive frequency
 Source: How does a fluxgate sensor work? - ICL
Source: How does a fluxgate sensor work? - ICL
Typically, 3 fluxgates are attached to measure magnetic fields in all the three axes
Attitude Determination using Fluxgates
A fluxgate alone can only deliver coarse attitude information. This is done by measuring the time derivative of the magnetic field. Usually, without any gyroscopes, the acquired information is only coarse and not 100% accurate. However, an extended Kalman filter can be used1